Thread identification guide
STEP 1
Determine if the thread is tapered or parallel/straight.
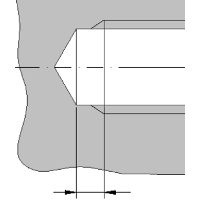
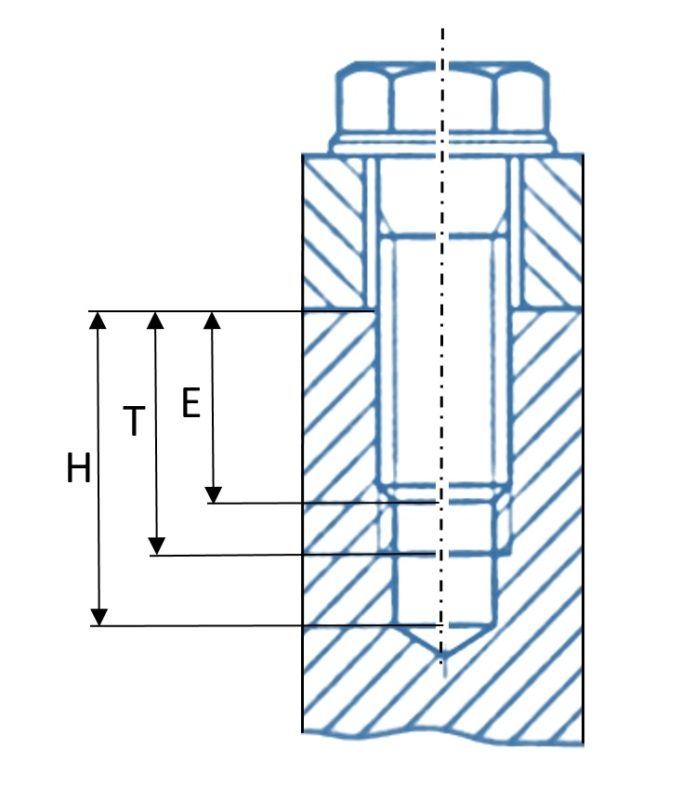
Measure the thread with a caliper at the beginning and the end. If the diameters increase for a male end or decrease for a female end, the thread is tapered. If it is the same value the thread is straight/parallel.

STEP 2
Determine the thread size and type. Imperial sizes are normally common fractions ¼”=0.25”.
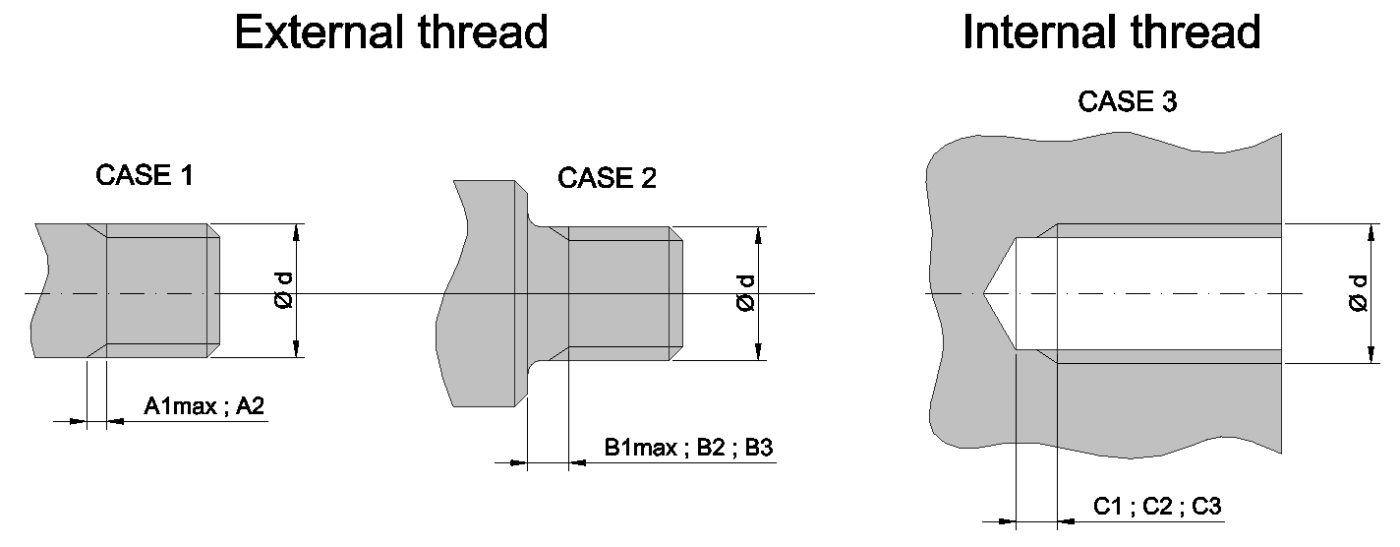
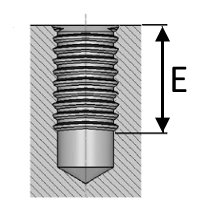
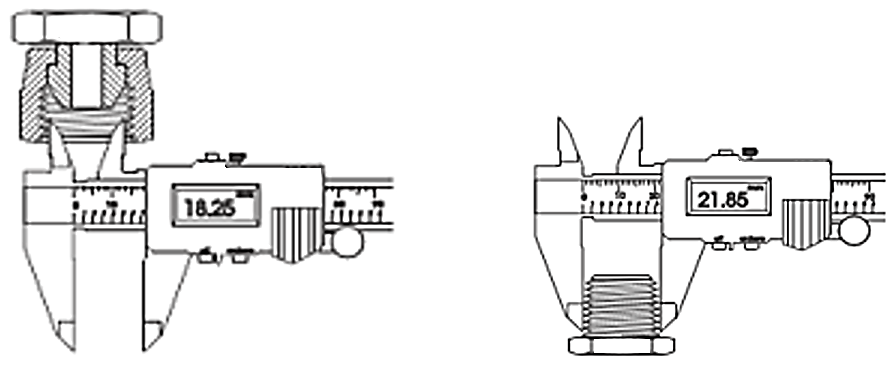
Measure the outside diameter OD for male and inside ID for female threads.
If the thread is tapered measure the diameter of 4th or 5th full thread.
The diameter measurement obtained in this step may not be exactly the same as the listed nominal size for the given thread. This variation is due to manufacturing tolerances.
STEP 3
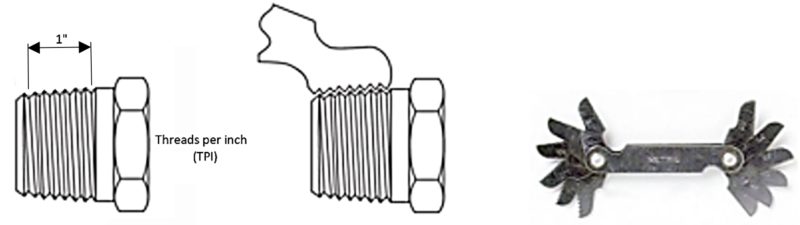
Determine the pitch for metric or the amount of threads per inch (T.P.I) for imperial sizes.
In both cases Thread pitch gauges can be used.
| TPI | 28 | 27 | 24 | 20 | 19 | 18 | 16 | 14 | 12 | 11.5 | 11 | 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thread pitch (mm) | 0.91 | 0.94 | 1.06 | 1.27 | 1.34 | 1.4 | 1.59 | 1.81 | 2.12 | 2.21 | 2.31 | 3.18 |
Check for any markings on fitting or equipment which may be a clue to thread type. Country of origin may provide a clue.
Europe (DIN,BSP), America (NPT, JIC, UNO, ORFS), UK/Australia (BSP), Japan (JIS).