Flow Conversions (Actual, Normal and Standard Conditions for Pressure and Temperature)
ACTUAL FLOW RATE is the actual volume of fluid that passes a given point in a pipe per unit time e.g. l/min. This can be a useful measurement to have, however since gases are compressible the volume of gas will vary depending on its pressure and temperature. Therefore it is generally more useful to have a flow rate referenced to a set pressure and temperature, hence the use of Standard flow rate, and Normal flow rate.
These units are corrections applied to an actual flow measurement based on a given temperature and pressure. The correction is applied using the ideal gas law.
This allows us to compare different flows existing at different flowing conditions of pressure and temperature.
However, the problem with Standard and Normal conditions is that they have several different definitions depending on the industry you work in, and in the country you work.
NORMAL CONDITIONS FOR TEMPERATURE AND PRESSURE (NCTP, common in Europe)
Commonly used as a standard condition for testing and documentation of fan capacities
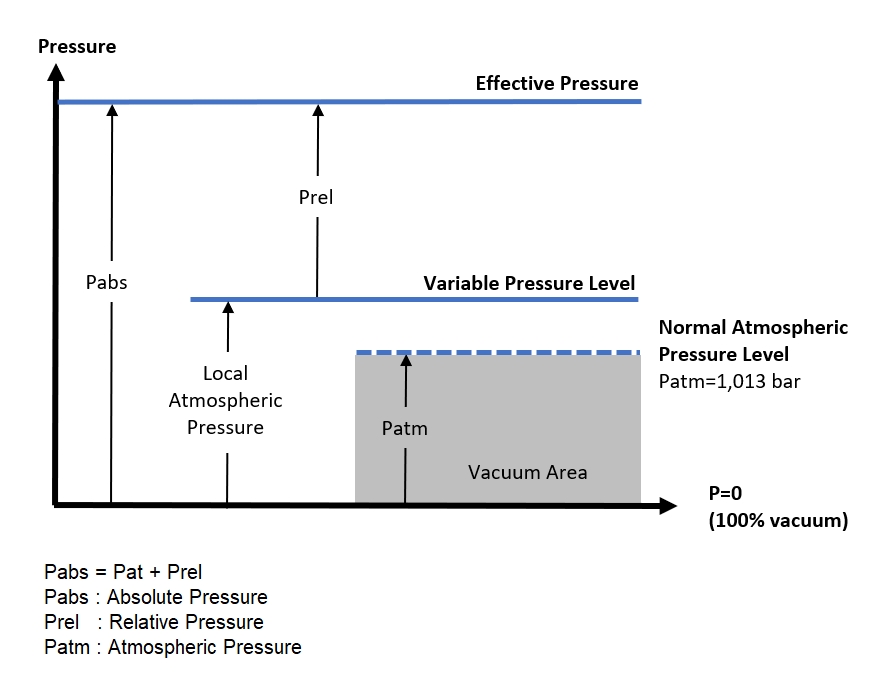
NTP is defined as a temperature of 20 °C (293.15 K, 68 °F) and an absolute pressure of 1 atm (1,013 bar, 101,325 kPa).
Flow Rate Units e.g.:
Normal litre per minute (NLPM)
STANDARD CONDITIONS FOR TEMPERATURE AND PRESSURE (SCTP, common in the United States)
important for the measurements and documentation of chemical and physical processes
Until 1982, STP was defined as a temperature of 273.15 K (0 °C, 32 °F) and an absolute pressure of 101.325 kPa (1 atm).
Since 1982, STP is defined as a temperature of 273.15 K (0 °C, 32 °F) and an absolute pressure of 100 kPa (1 bar).
Flow Rate Units e.g.:
Standard litre per minute (SLM or SLPM)
Standard cubic feet per minute (SCFM)