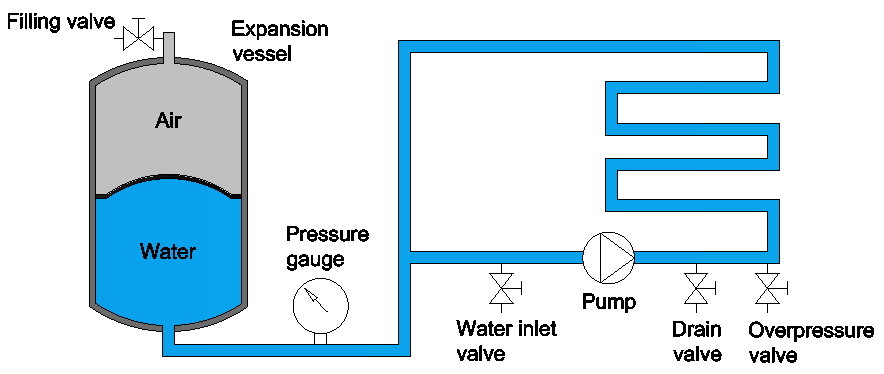
Water expansion vessel
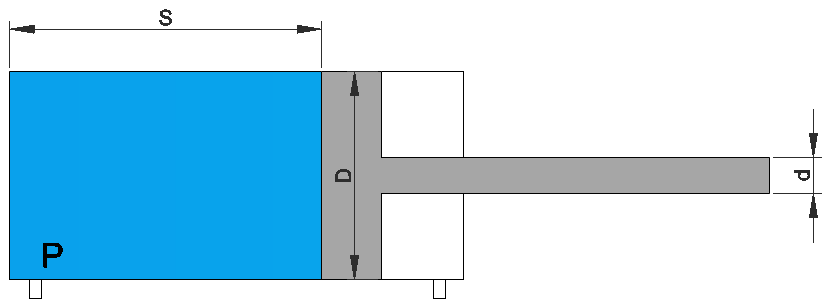
This calculation is for a snap-fitting hook of rectangular cross section.There are two types which can be choosen for the calculation. Type 1 is a snap-fitting hook of a constant rectangular cross section and Type 2 is a snap-fitting hook of rectangular cross section with a constant decrease in thickness from h at the root to h/2 at the end of the hook. Young modulus and Yield strength of the material have to be choosen. The Deflection Force is the force required to bend the arm the value of the introduced deflection (y). Introducing the friction coefficient of the material and the angle of the arm according with the shape represented in picture, the mating force is calculated. This is the force required for introducing the snap-fitting hook. The calculus allows to ensure that the yield strength of the material won’t be exceeded as long as the safety coeficient is higher that 1. This calculation is an approximation because of we are only taking into account the shear due to bending.
| Product | Dynamic viscosity [cP] | Temperature [C] |
|---|---|---|
| Air | 0.01 | 21 |
| Caulking Compound | 5.000.000-10.000.000 | 25 |
| Chocolat | 25000 | 21 |
| Cream | 100000 | 21 |
| Crisco Shortening or Lard | 1.000.000-2.000.000 | 25 |
| Ethylene glycol | 15 | 21 |
| Honey | 2.000 to 10.000 | 21 |
| Melted polymers | 1000000 | 21 |
| Methanol | 0.5 | 21 |
| Milk | 3 | 21 |
| Mustard | 70000 | 21 |
| Peanut butter | 250000 | 21 |
| Rubber compounds | 5000000 | 21 |
| SAE 10 motor oil | 80 to 140 | 21 |
| SAE 20 motor oil | 140 to 420 | 21 |
| SAE 30 motor oil | 420 to 650 | 21 |
| SAE 40 motor oil | 650 to 900 | 21 |
| Tomato sauce | 50000 | 21 |
| Water | 1.3059 | 10 |
| Water | 1.0016 | 20 |
| Water | 1 | 21 |
| Water | 0.79722 | 30 |
| Water | 0.54652 | 50 |
| Water | 0.40355 | 70 |
| Water | 0.31417 | 90 |
| Window Putty | 100000000 | 25 |
| Wine | 25 | 21 |
This calculator is valid for simple and double effect. For simple effect the value provide by the calculator has to be divided by 2.
Leakage is not taken into the calculator.
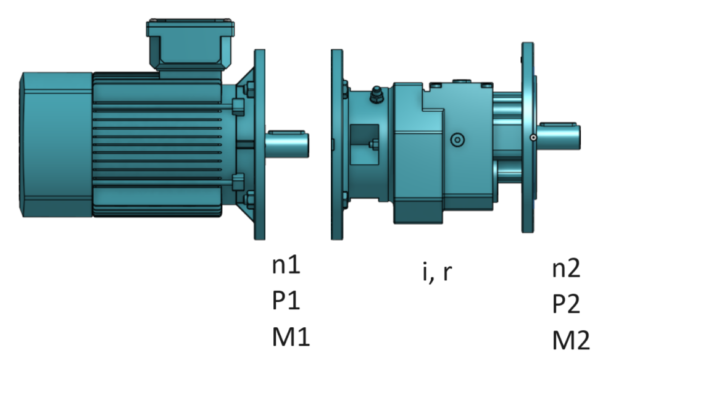
The system represented consists of an electric motor and a gearbox. The calculator is designed to obtain the technical specifications at the output of the gearbox. To use this calculation tool, input data as detailed in the following protocol:
MOTOR:
From these inputs, the calculator will generate the Nominal Torque, which will display the nominal torque the motor can develop based on the input rotational speed and power.
GEARBOX:
Input information pertaining to the gearbox that will be connected to the motor.
OUTPUT: