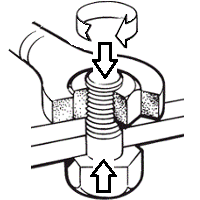
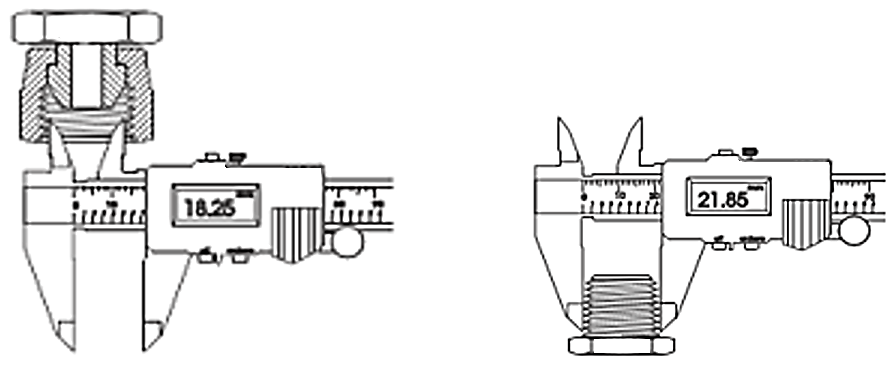
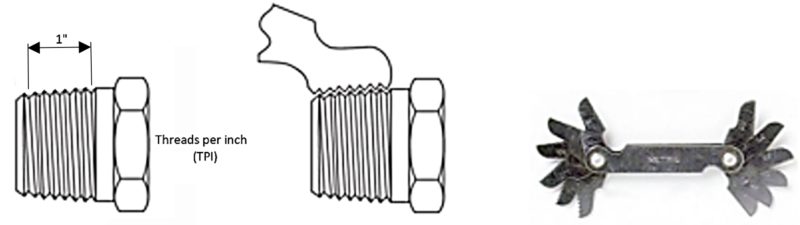
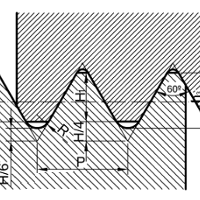
| A/B | 60° | Parallel | DIN 4503, ISO 1222 | Tripod connection thread | Connections to photografic equipment. |
| ACME-C | 29° | | ANSI B1.5 (1977) | Acme thread centralizing | |
| ACME-G | 29° | | ANSI B1.5 (1977) | Acme thread general purpose | |
| AMO | 55° | | ANSI B1.11 (1958) | American standard microscope objective thread | |
| ANPT | 60° | | MIL-P-7105 | Aeronautical national form taper pipe thread | |
| API | 60° | | | American national taper form thread for petroleum installations | |
| BA | 47°30' | | BS93 (1951) | British association thread | |
| BSC | 60° | | BS811 (1950) | British norm thread for bicycles | |
| BSF | 55° | Parallel | BS84 (1956) | Whithworth fine thread | |
| BSW | 55° | Parallel | BS84 (1956) | Whithworth coarse thread | |
| E | - | | DIN 40400, DIN 49612, DIN 49610, DIN 49625 | Edison form thread | Electrical thread. |
| EG M | 60° | Parallel | DIN 8140-2 | Metric ISO thread for helical coil wire screw thread inserts | For wire thread inserts. |
| EG-UNC | 60° | Parallel | MS 33537 | Unified coarse thread series for helical coil wire screw thread inserts | |
| EG-UNF | 60° | Parallel | ASME B18.29.1 | Unified fine thread for helical coil wire screw thread inserts | |
| FG | 60° | Parallel | DIN 79012 | Bicycle thread | For cycles and motor-scooters. |
| G | 55° | Parallel | DIN ISO 228, DIN 6630 | Pipe parallel ISO thread | For pressure tight joints are not made on the thread. External and internal pipe thread. Packaging; external thread for barrels. |
| G | 55° | Parallel | BS2779 (1973) | Pipe whitworth thread (BSP)parallel | |
| Gf | | Tapered | DIN 4930 | Round tapered thread | Tubes and tunneling |
| Gg | 60° | Tapered (1:16) | DIN 4941 | Tapered thread | For drill pipes in water and rock drilling, mining. |
| Gg | 30°-30° | Tapered (1:4) | DIN 20314 | Tapered thread | For drill pipes in water and rock drilling, mining. |
| GL | 30°-60° | Parallel | DIN 168-1 | Cylindrical round thread | For glass containers. |
| Glasg | 30°-50° | Parallel | DIN 40450 | Glasg thread for glass | Electric industry: glass fittings, protection glasses. |
| HA-HB | | | DIN 58810 | Bone screw thread | For surgical implants, external and internal thread. |
| KT | 20° | Parallel | DIN 6063 | Trapezoidal thread | Preferably for packages made of plastics. |
| LN | 60° | Parallel | LN 9163, EN 2158 | ISO Metric thread for aviation | Aviation and aerospace. |
| M | 60° | Parallel | DIN 13, DIN 14, ISO 68, DIN 6630, LN 9163, DIN 2510 | Metric coarse ISO thread | General engineering, watches, fine work, packaging; external thread for barrels, aviation, aerospace and bolted connections with reduced shank. |
| M | 60° | Tapered (1:16) | DIN 158 | Taper metric ISO thread | Plugs and grease nipples. |
| MF | 60° | Parallel | DIN 13, DIN EN 60423 | Metric fine ISO thread | |
| MFS | 60° | Parallel | DIN 8141-1 | ISO Metric thread for tight fit | |
| MJ | 60° | Parallel | DIN ISO 5855 | Metric ISO thread for aeronautics | Aviation and aerospace. |
| N | 60° | | ANSI B1.1 (1960) | American national 8-12-16 TPI pitch series (8N, 12N, 16N) | |
| N-BUTT | 45°+5° | | ANSI B1.9 (1973) | American BUTTRESS thread | |
| NC | 60° | | ANSI B1.1 (1960) | American national coarse thread series | |
| NEF | 60° | | ANSI B1.1 (1960) | American national extra fine thread series | |
| NF | 60° | | ANSI B1.1 (1960) | American national fine thread series | |
| NGO | 60° | | ANSI/ASME-B1.20.1 (1983) | National gas outlet thread (specify RH or LH) | |
| NGS | 60° | | ANSI/ASME-B1.20.1 (1983) | National gas straight thread | |
| NGT | 60° | | ANSI B57.1 (1977) | National gas taper thread (see also SGT) | |
| NH | 60° | | ANSI B2.4 H28 (1966) | American national firehouse and hose coupling thread | |
| NPS | 60° | | | American standard straight pipe thread NSPC & NPSM | |
| NPSC | 60° | | ANSI/ASME-B1.20.1 (1983) | American standard straight pipe thread in pipe couplings (marked NPS) | |
| NPSF | 60° | | ANSI B1.20.3 (1976) | Dryseal American standard internal straight pipe thread (fuel) | |
| NPSH | 60° | | ANSI/ASME-B1.20.1 (1983) | American standard straight pipe thread for hose couplings | |
| NPSI | 60° | | ANSI B1.20.3 (1976) | American standard intermediate internal straight pipe thread | |
| NPSL | 60° | | ANSI/ASME-B1.20.1 (1983) | American standard straight pipe thread for loose-fitting mechanical joints | |
| NPSM | 60° | | ANSI/ASME-B1.20.1 (1983) | American standard straight pipe thread for free-fitting mechanical joints | |
| NPT | 60° | Tapered (1:16) | ANSI/ASME-B1.20.1 (1983) | American standard tapered pipe thread | For threads with dryseal material. |
| NPTF | 60° | Tapered (1:16) | ANSI B1.20.3 (1976) | American standard tapered pipe thread (fuel) | For threads without dryseal material. |
| NPTR | 60° | | ANSI/ASME-B1.20.1 (1983) | American standard taper pipe thread for railing joints (tap market NPT) | |
| NS | 60° | | ANSI B1.1 (1960) | American national thread special pitches | |
| Pg | 80° | Parallel | DIN 40430 | Steel electrical conduit thread | For electric installations. |
| PTF | 60° | | ANSI B1.20.1 (1976) | Dryseal SAE short taper pipe thread | |
| R | 55° | Parallel | DIN 259 | Pipe parallel whitworth thread | For pressure tight joints are not made on the thread. Piping, do not use in new designs. |
| R | 55° | Tapered (1:16) | BS21 (1985), DIN EN 10226-1, ISO 7-1, DIN 2999, DIN 3858 | External dryseal pipe taper thread (BSPT) | Tapered Whitworth pipe thread where pressure-tight joints are made on the threads. |
| Rc | 55° | Tapered (1:16) | BS21 (1985), DIN EN 10226-1, ISO 7-1 | Internal dryseal pipe taper thread (BSPT) | Tapered Whitworth pipe thread where pressure-tight joints are made on the threads. |
| Rd | 30° | Parallel | DIN 405, DIN 20400, DIN 15403, DIN 7273 | Rounded thread | General, for mining industry, for lifting hooks, for steel sheet items and related joints. |
| RMS | 55° | Parallel | DIN 58888 | RMS-thread | Objective for microscope. |
| Rp | 55° | Parallel | DIN 2999, DIN 3858 | Internal dryseal parallel thread | Internal thread for pipes and fittings. |
| Rp | 55° | Parallel | BS21 (1973), DIN EN 10226-1, ISO 7-1 | Pipe parallel thread (BSPP) | Cylindrical Whitworth pipe thread where pressure-tight joints are made on the threads. |
| S | 30°+3° | Parallel | DIN 513, DIN 20401 | Saw form thread | General. Mining industry. |
| S | 45° | Parallel | DIN 2781 | Saw form thread | For machine tools, hydraulic presses. |
| S | 105° | Tapered (7°30') | DIN 71412 | Self forming taper external thread | Taper lubricating nipple. Similar to DIN 158 but 105° thread angle. |
| SB | | | | Manufacturers stovebolt standards thread | |
| SGT | 60° | | ANSI B57.1 (1977) | Special gas taper thread | |
| SPL-PTF | 60° | | ANSI B1.20.3 (1976) | Dryseal special taper pipe thread | |
| ST | 60° | Parallel | DIN 7970, DIN EN ISO 1478 | Sheet metal screw thread | For tapping screws. |
| STI | 60° | | | Special thread for helical coil wire screw thread inserts | |
| STUB-ACME | 29° | | ANSI B1.8 (1977) | Stub Acme thread | |
| Tr | 30° | Parallel | DIN 103, DIN 380, DIN 263, DIN 6341, DIN 30295 | Trapezoidal thread | General, for rail vehicles, for collet chucks. |
| UN | 60° | | ANSI B1.1 (1982) | Unified 8-12-16 TPI pitch series | |
| UN-8 | 60° | | ASME B1.1 | Unified thread for special diameters and pitches | |
| UNC | 60° | | ANSI B1.1 (1982) | Unified coarse thread series | |
| UNEF | 60° | | ANSI B1.1 (1982) | Unified extra fine thread series | |
| UNF | 60° | | ANSI B1.1 (1982) | Unified fine thread series | |
| UNJ | 60° | | BS 4048 (1978) | Unified constant pitch with a 0,15011P to 0,18042P controlled root radius | |
| UNJC | 60° | | BS 4048 (1978), ASME B1.15 | Unified coarse thread with a 0,15011P to 0,18042P controlled root radius | |
| UNJEF | 60° | | BS 4048 (1978) | Unified extra fine thread with a 0,15011P to 0,18042P controlled root radius | |
| UNJF | 60° | | BS 4048 (1978), ASME B1.15 | Unified fine thread with a 0,15011P to 0,18042P controlled root radius | |
| UNM | 60° | | ASA B1.10 (1958) | Unified miniature thread series | |
| UNS | 60° | | ANSI B1.1 (1982) | Unified thread special pitches | |
| V | 60° | | | 60° "V" thread with truncated crest and root(flatted to the user's specifications) | |
| Vg | 60° | Parallel | DIN 7756 | Valves thread | Valves for tires. |
| W | 55° | Parallel | DIN 477 | Parallel whitworth thread | Cylindrical thread for side connections. |
| W keg | 55° | Tapered (3:25) | DIN 477, DIN EN 144-1, DIN EN 629-1, DIN EN ISO 11116-1 | Tapered thread for screw sockets | Gas cylinders, thread for side nozzles. |